Blue Screen While Playing Games: 10+ Best Fixes You Should Try
13 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
If you experience a blue screen while playing games, it indicates your Windows PC is going through hardware or software issues.
To make matters worse, a blue screen of death (BSOD) shows up more often when you’re playing mid to high-end PC games.
Find below the tried and tested methods to troubleshoot the issue yourself. The steps mentioned below are compatible with both Windows 11 and 10 PCs.
Blue Screen While Playing Games – What Is It?
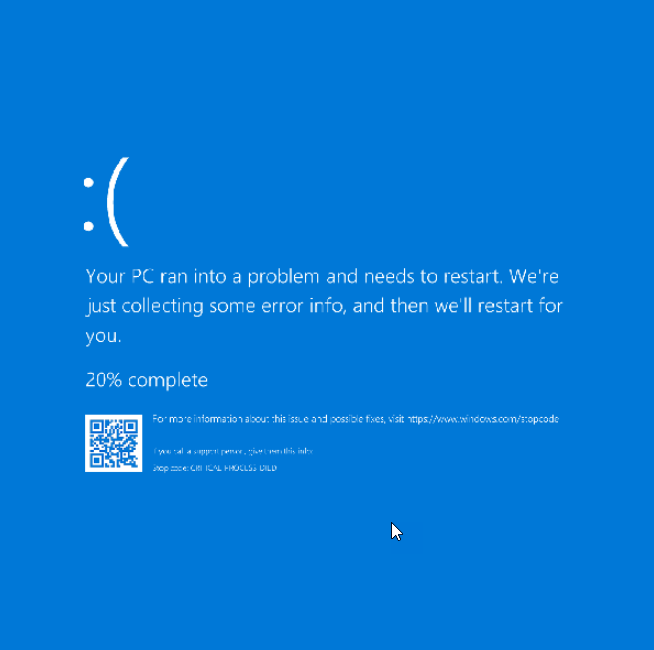
A BSOD is an error screen that happens to prevent further major damage to the whole computer. When playing a PC game, you might experience the game freezing, the screen blinking a few times, and then the characteristic blue screen.
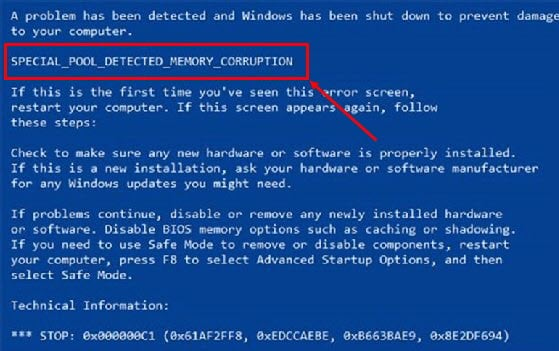
It’ll often show you the exact issue in the following codes.
Sometimes, you might not see any error codes as none are available or the BSOD screen reboots to Legacy or UEFI BIOS quickly.
If you see this once or twice in a few months, you must take measures to prevent future system damage. Contrarily, if the BSOD keeps showing up, you can take no intermediate steps other than going directly to the troubleshooting ideas below.
How To Fix Blue Screen While Playing Games
I’ve arranged these troubleshooting methods in order of simplicity. This way, if a minor bug causes the BSOD error, you can quickly resolve it with minimal effort.
Run Windows in Safe Mode
You can do the following if the BSOD error shows up repeatedly or once in a while:
- Boot up your PC.
- Wait till you see the Windows logo and press the power or reboot button to restart the device.
- Repeat the process once again.
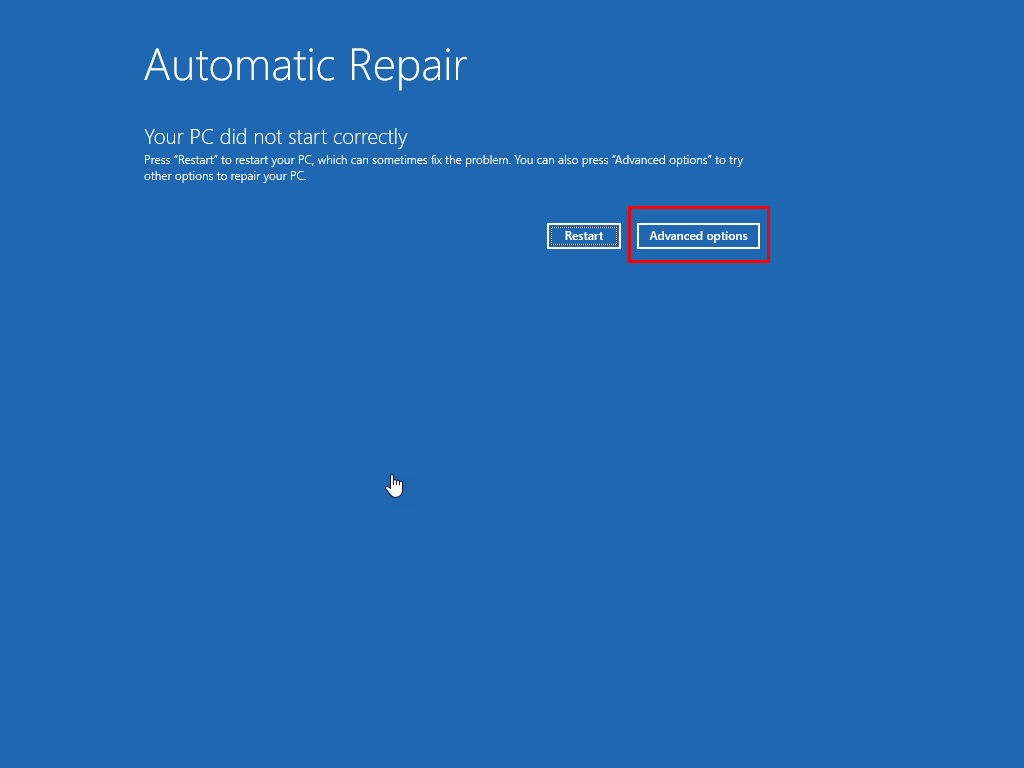
- You should now see the following screen along with the Windows logo:
- On the Automatic Repair screen, click on the Advanced options button.
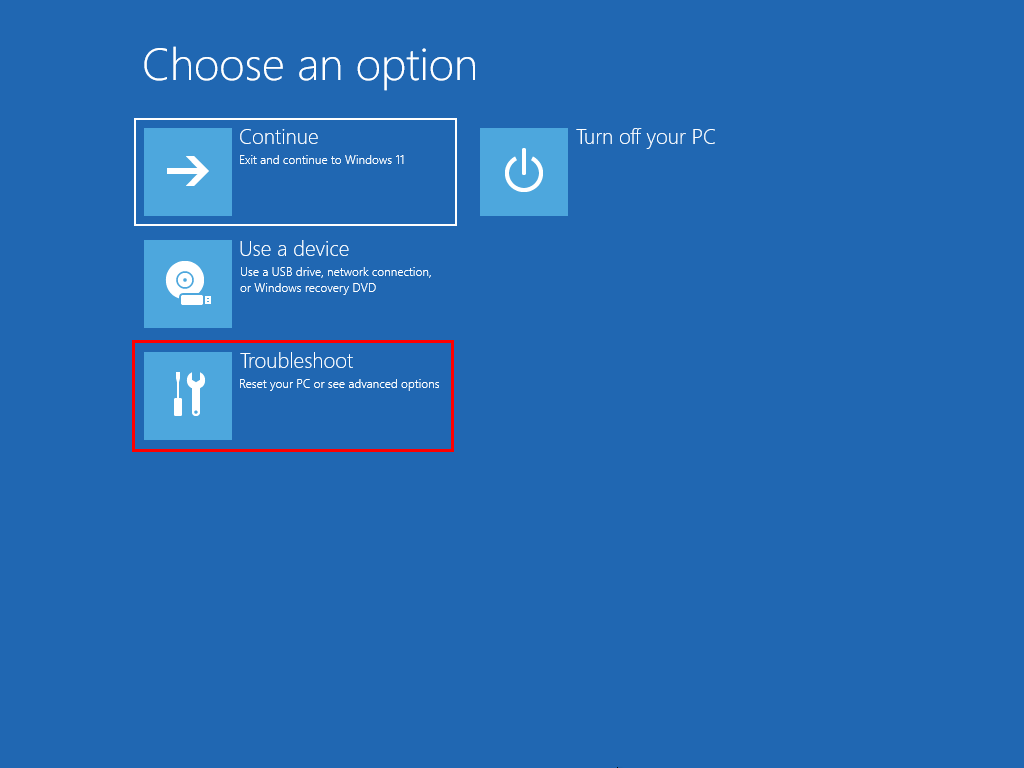
- Select the Troubleshoot menu in the Choose an option screen.
- Click on the Advanced options button in the Troubleshoot window.
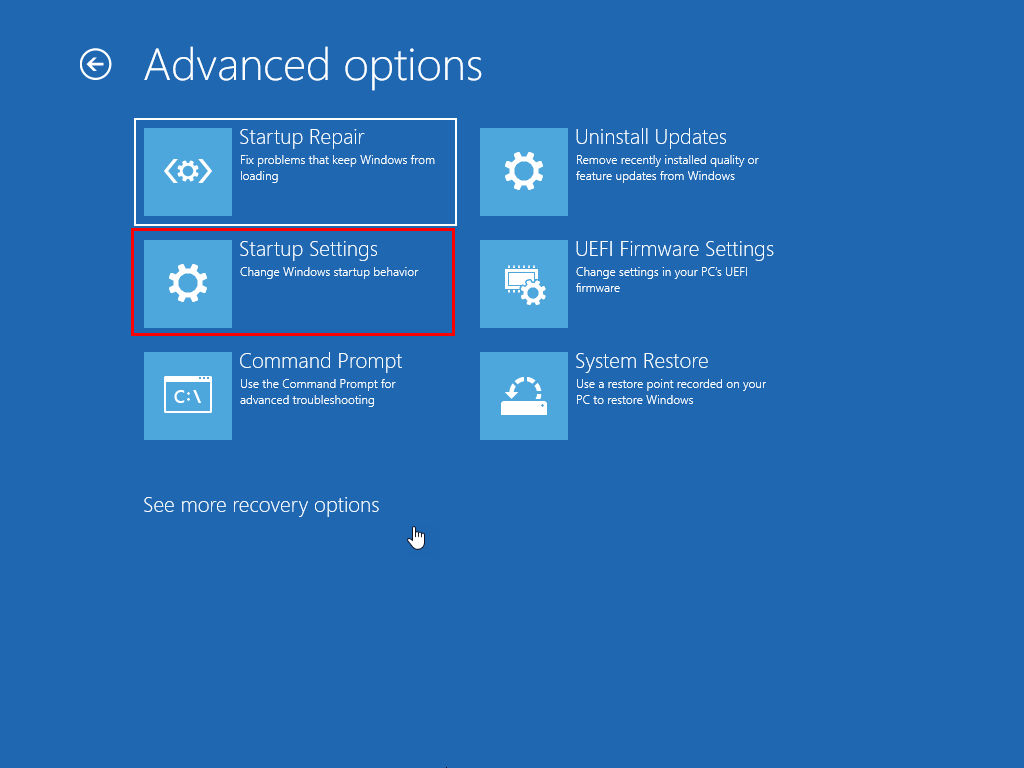
- Select Startup Settings on Advanced options.
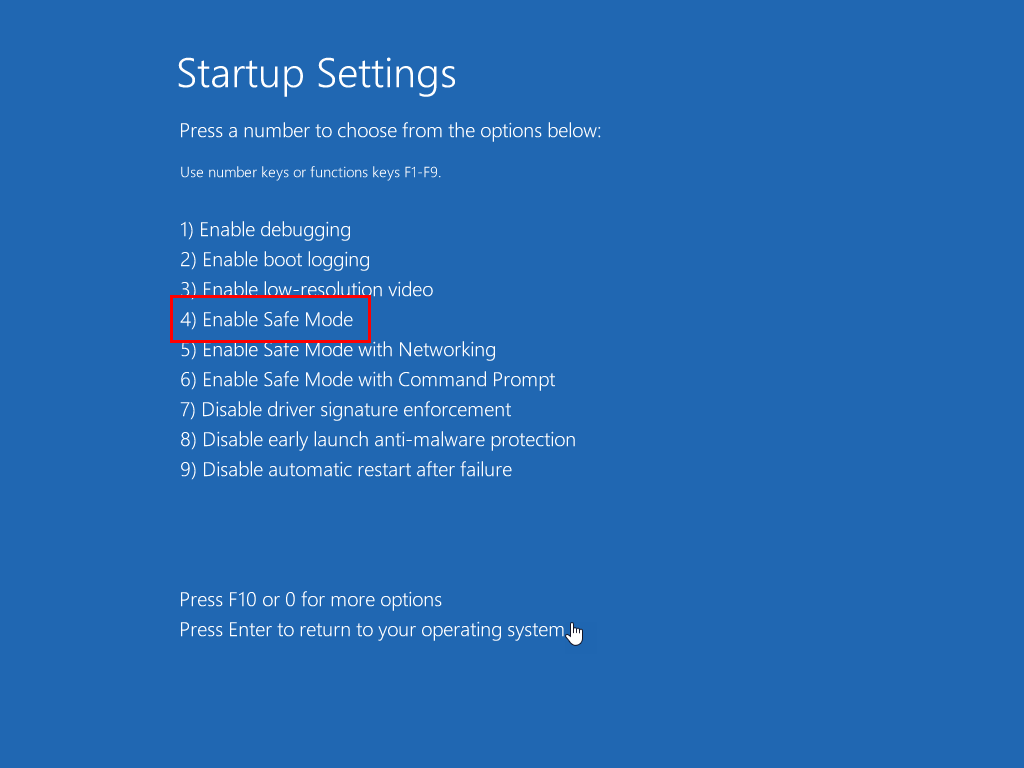
- Click the Restart option in the Startup settings screen.
- After the reboot, when you see the Startup Settings window, press 4 to enter Safe Mode.
Try out different tools in your Windows PC in Safe Mode. Keep it up and running for a few hours. Are you able to reproduce the BSOD error?
If your answer is “No“, it’s an app-specific issue. The application might not be compatible with your PC. Reach out to the specific PC game’s support team for further assistance.
If the BSOD shows up in Safe Mode during the test period, continue with the rest of the troubleshooting methods.
Stop Overclocking
If you overclock any or all of the following hardware of your Windows PC, you should stop as soon as you encounter a BSOD:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit or Card)
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- Motherboard: hardware voltage and voltage multiplier settings
- Storage Devices like NVMe SSDs (disabling thermal throttling).
If you’ve overclocked your CPU, here’s how you can undo that:
- Reboot your PC to access the BIOS setup menu using a specific key, like F2, F10, or Delete. These buttons will depend on your motherboard. Find below a list of the BIOS keys for different mainboard manufacturers:
- Asus: Delete + F2
- ASRock: F2 or Del
- Foxconn: F8
- MSI: Delete or F2
- Gigabyte: F2 + Del
- Biostar: Delete + F8
- EVGA: Delete or F2
- HP: F10
- Some mainboards will display the BIOS key on the POST screen.
- Find the menu in the BIOS for overclocking settings. Usually, it’s named as either Overclocking or OC Tweaker.
- Find the menu showing the settings for CPU clock speed, multipliers, and voltage, labeled as CPU Ratio, CPU Core Voltage, or Vcore.
- Set them all to Auto or Default to return the CPU to its original specifications.
- Save changes and exit BIOS to disable overclocking settings.
De-overclocking options for the RAM chips, NVMe SSD chips, and the mainboard should also be in the BIOS.
However, you might want to try overclocking software for better control over this process.
Optimize In-Game Graphics Settings
You can reduce the game app’s visual quality. It’ll reduce the requirements of CPU, RAM, and GPU bandwidth and prevent BSODs. Here’s how:
- Run the game app.
- Quickly go to the Options or Game Settings.
- Locate options that relate to graphics, visual quality, etc., and click on them. In this guide, it’s the Graphics Options button.
- Reduce the values for the following components:
- Resolution
- Frame rate
- SSAA
- Particle quality
- Dynamic lighting
- Fog of war/blur/ motion blur/ bloom/ glare
- Shaders
- Foliage
- Water
- Shadows
- Textures
- Disable VSYNC, Anti-Aliasing, Shader 12.0, etc.
- Save the changes you’ve made.
- Close and re-launch the game app.
- Check if the blue screen while playing games persists.
Check if the GPU and CPU Are Overheating
First, you should get the HWiNFO app and install it on your PC.
Then, you must find out the idle temperature of your CPU and GPU by following these steps:
- Run the HWiNFO app from the Start Menu.
- Click the Start button on the dialog that shows up.
- The HWiNFO Sensor Status window will open.
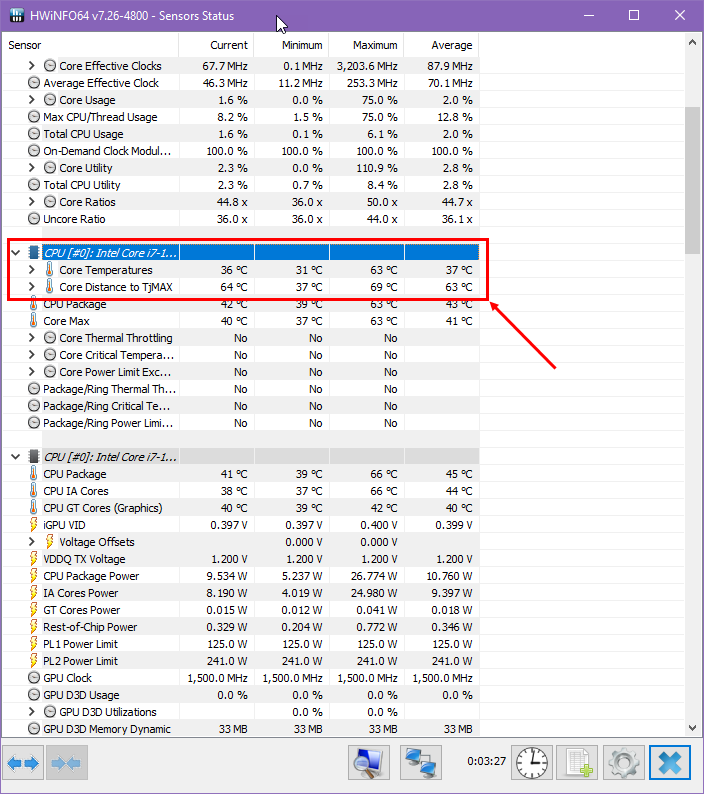
- Scroll down to the CPU [#0] that shows the following items:
- Core Temperatures
- Core Distance to TjMAX
- Write down the values shown there. They represent the idle temperature of your CPU.
- Scroll down further to locate the GPU [#1] section.
- Note the values indicated in the following bullets:
- GPU Temperature
- GPU Hot Spot Temperature.
This is how hot the graphics card is when it’s in the idle mode.
Now, run the PC game you’ve been playing earlier when the BSOD error appeared. Keep playing for a few minutes and quit the game before another error shows up.
Immediately open the HWiNFO app and look at the temperature values for the CPU and GPU.
If the values are like this, the BSOD is due to overheating:
- For a CPU of Tj Max (junction temperature) 100°C, the average temperature should be below 10 to 20 degrees of the Tj Max value. For instance, if you see 80°C to 90°C, it’s okay. However, if it’s more than 90°C to 100°C, there’s an overheating problem. You can search Google to find the Tj Max value of your CPU.
- For GPUs, the average temperature when gaming shouldn’t go above 80°C to 90°C.
You might want to look for professional help to cool down your PC case. This will help dissipate the heat generated by CPU and GPU when you run high-end PC games or software.
Kill Needless Background Processes
You can end unnecessary background processes to free up more memory on the PC. Do this right before launching the game app:
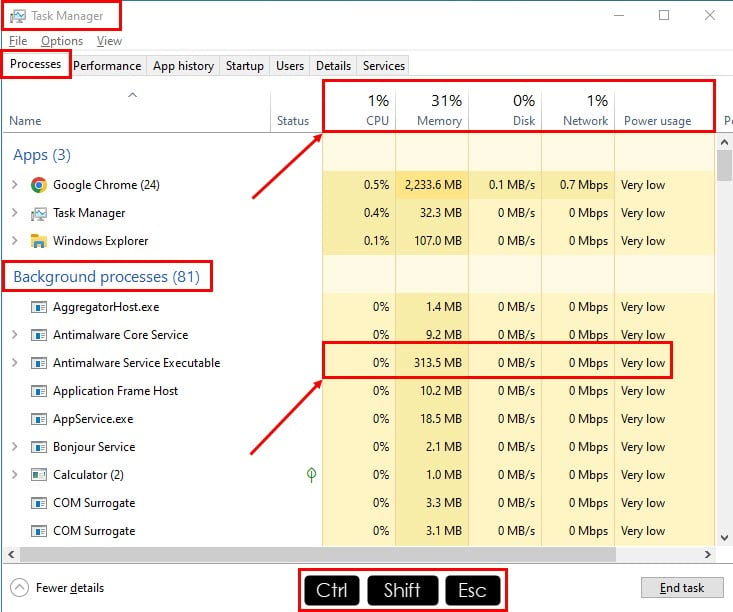
- Open the Task Manager tool by pressing the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys.
- You’ll see multiple sections in the Processes tab. You’ll find the individual processes below them.
- Go to the Background processes header and scroll down.
- You should look for options that consume the most CPU, Memory, and similar resources.
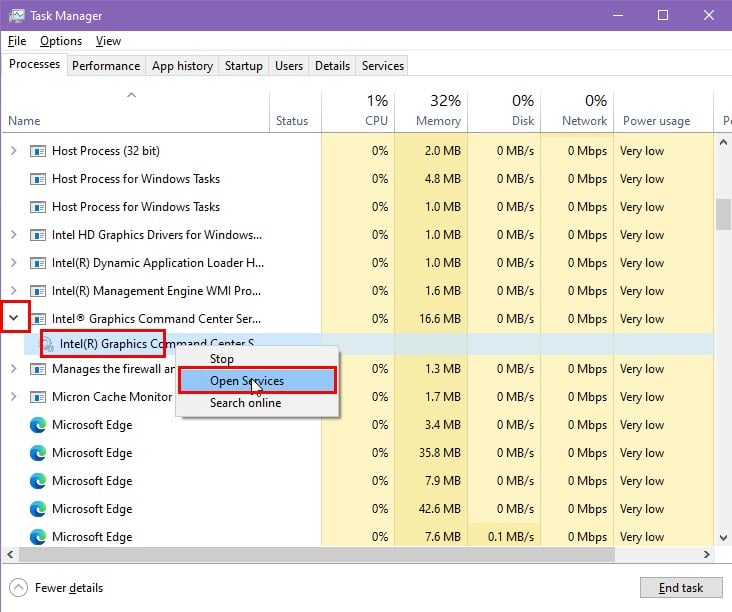
- Click on the extension drop-down arrow to the left of the selected process to reveal the underlying service.
- Right-click on the service name and choose Open Services in the context menu.
- On the Services app interface, type the initial letter of its name.
- Find the exact service you’ve seen in the Task Manager.
- Right-click on that and choose Properties from the context menu.
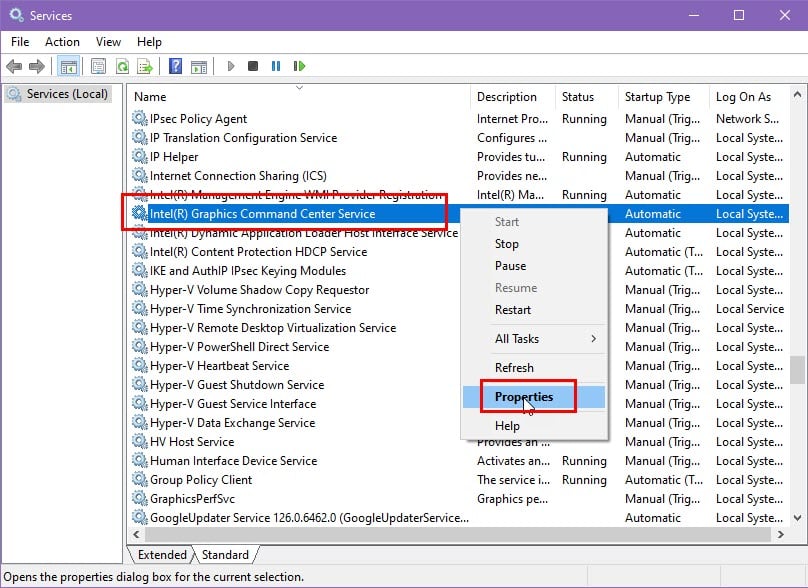
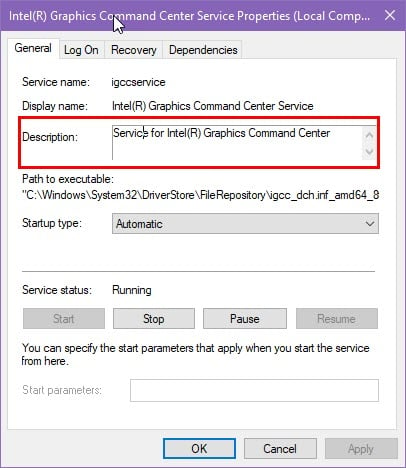
- You’ll see a new dialog box. There, you should see the Description of the service.
- The Description will tell you about the service, its functionalities, whether other apps are dependent on it, and more.
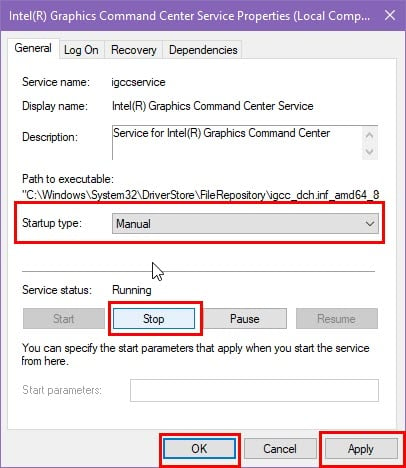
- If you find that it’s needless for the operating system or a high-end software/ PC game, you can stop this Windows 10 Service safely.
Run a Memory Diagnostic Test
You can often link BSOD errors during gaming to RAM or Memory failures.
Follow these steps to perform an exhaustive RAM chip test to find out if your Memory modules are healthy:
- Download the freeware version of MemTest86.
- You’ll get the memtest86-usb ZIP file.
- Create a new folder on your PC and name it MemTest86.
- Move the downloaded ZIP file to the above PC directory and extract all of its contents there.
- Plug in a USB drive. Ensure the USB stick is empty or you’re okay with formatting its contents.
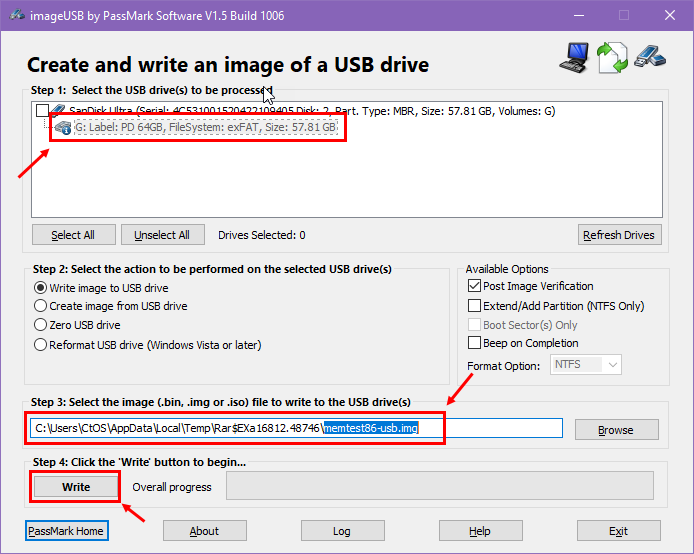
- Run the imageUSB app in the MemTest86 directory.
- Choose the USB stick in the list (Step 1).
- The image file, memtest86-usb.img, should already be selected by the imageUSB tool (Step 3).
- Click the Write button (Step 4).
So far, you’ve created a bootable USB drive. Your PC can use it to run the memory module scanning and evaluation process.
Now, follow these instructions to assess your RAM chips:
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS setup (usually by pressing a key like F2, F8, Delete, or Del during startup or POST).
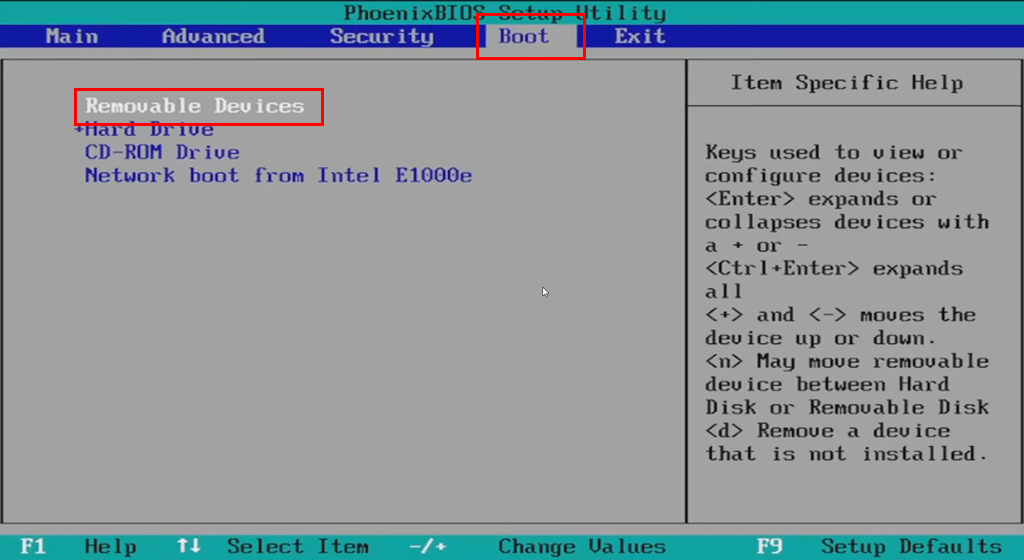
- Locate the boot order settings and change it to prioritize booting from the USB drive containing MemTest86.
- In the BIOS Boot tab, it’ll show as Removable Devices.
- MemTest86 should start automatically once the computer boots from the USB drive.
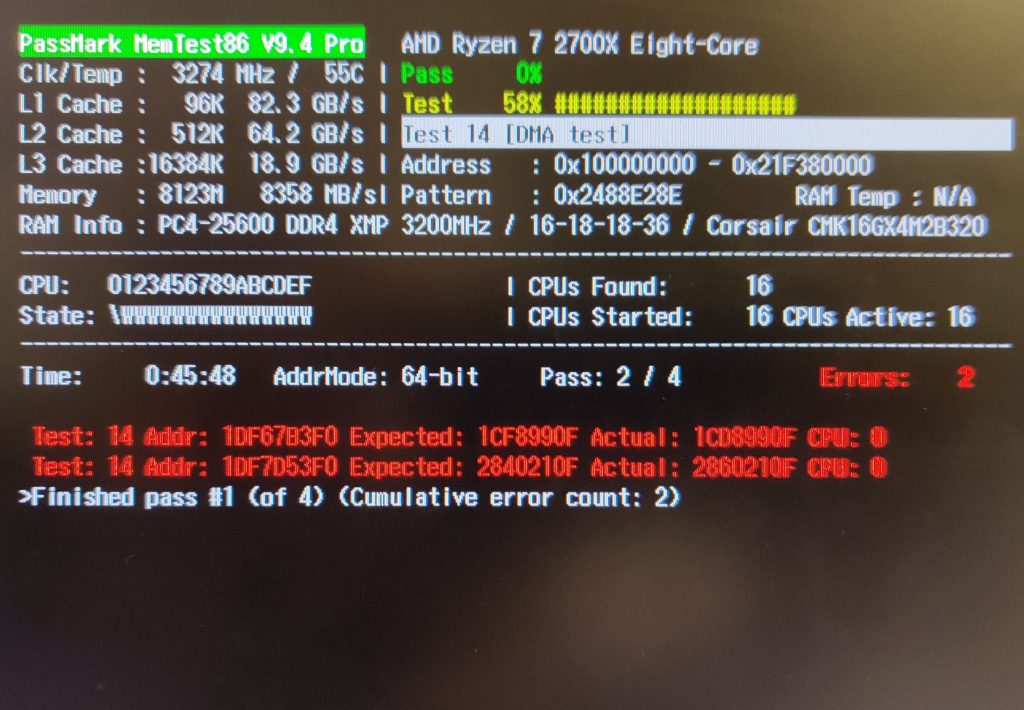
- By default, it runs 13 different tests, repeated 4 times each. This process can take several hours depending on your RAM amount and speed.
- In my case, it took 56 minutes per 8 GB RAM chips.
- MemTest86 will show the Pass or Fail statuses for your RAMs when the test is complete.
For BSOD cases related to RAM modules, it’s highly likely you’ll get a Fail notification. It might still be possible to run your Windows PC with these RAM chips.
However, memory-intensive processes, like playing high-end PC games or rendering 3D videos in Game Animation Software might show the BSOD error again. So, replace your RAM chips if you plan to utilize your PC’s full performance potential.
Run DISM and SFC Checks
When the Windows OS’s integrity is compromised, BSOD errors often appear. Follow these steps to evaluate and fix your OS integrity:
System File Checker (SFC) Check
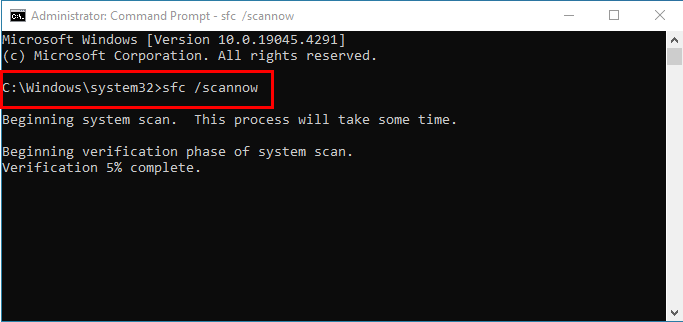
- Run the Command Prompt terminal app in administrator mode.
- Type the following command in the console and hit Enter:
sfc /scannow- Once the scan is complete, you’ll see a message saying that Windows Resource protection:
- …did not find any integrity violations: You don’t need to do anything.
- …found corrupt files and repaired them successfully: The issue is fixed automatically.
- …found corrupt files but was unable to fix some of them: Run the DISM check.
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Check
- Open Windows Command Prompt with elevated rights from the Start Menu.
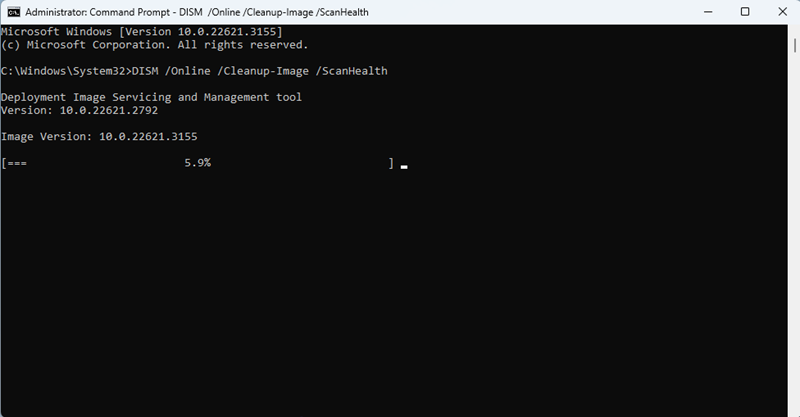
- Paste the following command inside the terminal and hit Enter:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth- The DISM scan can take some time to complete. The command prompt window will display the progress.
- Once the scan is finished, the Command Prompt window will show the results as outlined below:
- Scan finds no corruption: No component store corruption detected message is shown.
- If corruption is found: The Command Prompt might ask you to run the
RestoreHealthcommand to restore the system’s integrity.
Update the GPU Driver
If your GPU hardware driver is outdated, the GPU can’t keep up with the demands of high-end PC games.
You should update the driver by following these steps:
For NVIDIA
- Visit the NVIDIA Driver Downloads page.
- You can manually choose your graphics card type, operating system, and driver type (Game Ready Driver or Studio Driver) from the dropdown menus.
- Click the Search button to find compatible drivers.
- Alternatively, click the Automatically find drivers for my NVIDIA products button (if you see that) and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Once you have your driver, click the Download button.
- Save the downloaded file to a convenient location on your computer.
- Run the downloaded file to install the new driver.
- Restart your PC.
For AMD RADEON
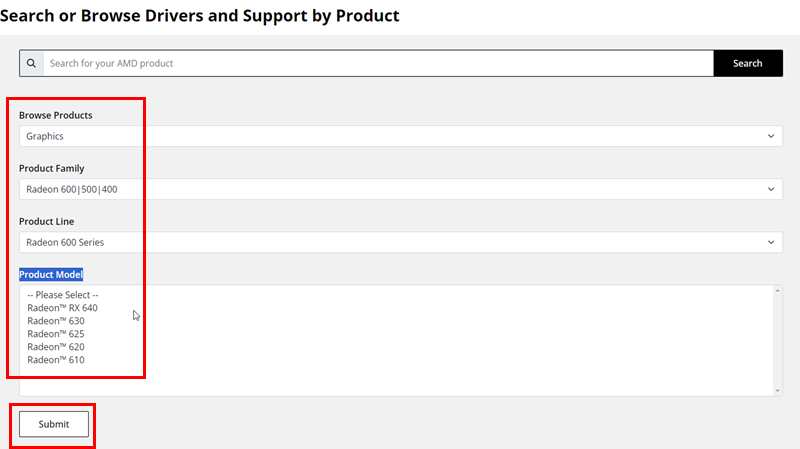
- Visit the AMD Driver and Support page.
- Go to the Search or Browse Drivers section and click on the Graphics option.
- Now, choose the specific Product Family relevant to your AMD GPU.
- Then, select the Product Line.
- You’ll see a concise list of Product Model numbers. Select one from the list.
- Finally, hit the Submit button.
- You’ll see the Drivers and Software screen.
- Click on the appropriate driver’s link to download.
- Install the driver package to update the AMD GPU driver.
Scan for Malware and Virus Programs
Malware, adware, spyware, and viruses might consume too much memory and CPU bandwidth on your PC when you’re playing a high-end PC game. Consequently, the system can’t allocate more RAM to the game.
So, you should perform an in-depth virus scan using the Windows Security app or any other antivirus software.
- Press the Windows + I keys to launch the Windows Settings app.
- Type Security in the Find a setting field and click on the Windows Security settings option.
- Click on the Virus & threat protection link in the Windows Security dialog box.
- The Virus & threat protection screen will open.
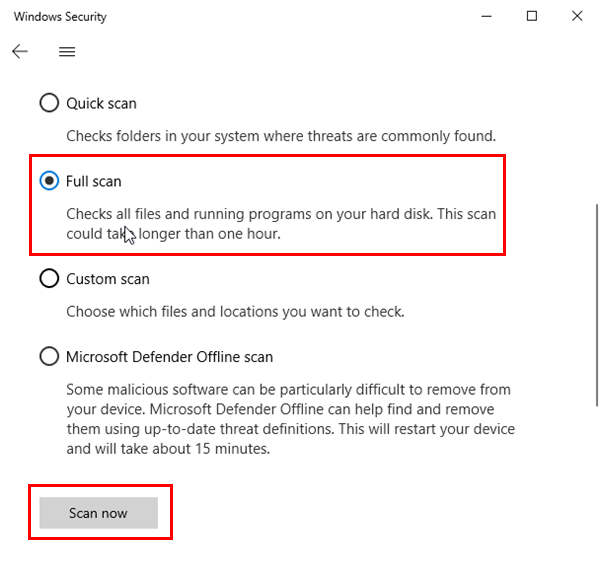
- There, click on the Scan options hyperlink.
- Select the Full scan option and hit the Scan now button.
- You’ll see the Full scan feature is running.
- The Windows Security tool will hunt down malware and viruses and eliminate those if there are any.
Flash Your BIOS Firmware
This is a delicate and risky process. Try these steps only if you’re absolutely sure that you can do exactly as instructed.
Before proceeding, fully charge if it’s a laptop or connect the desktop to an uninterrupted power supply line. If there’s any power interruption during the BIOS Flashing process, your motherboard will get bricked.
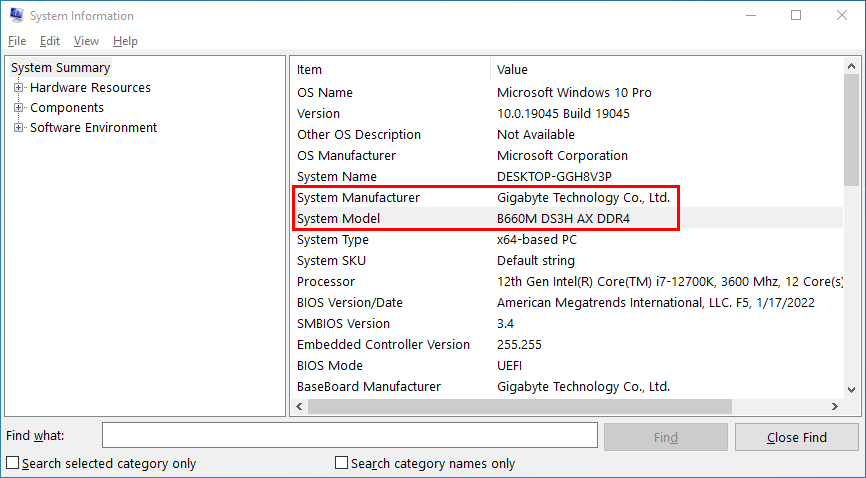
- Type System Information in the Start Menu.
- Click on the System Information app.
- On the System Summary, you should find the motherboard model name as the System Model component.
- Note down the name and model details accurately.
- Search Google with that model name.
- Open the official website.
- Click the Service or Support link on the website.
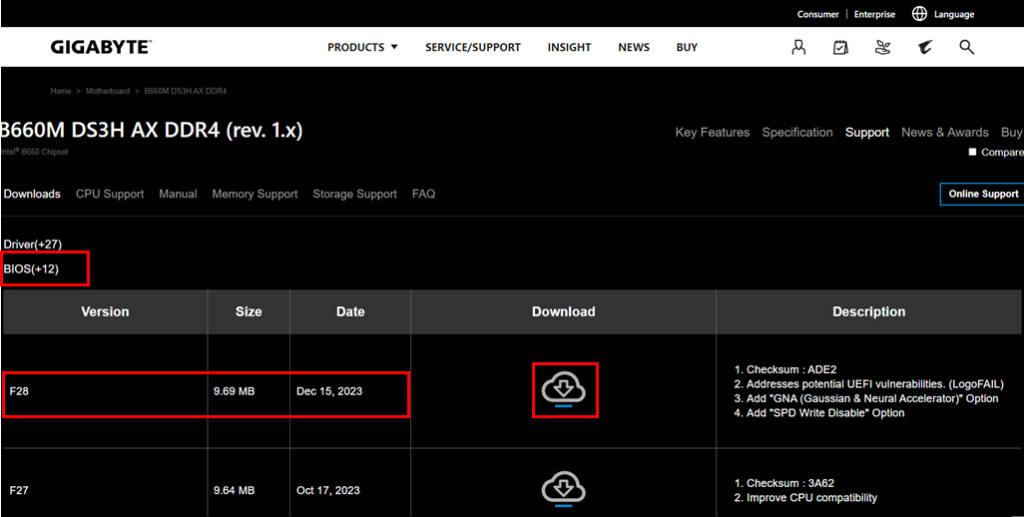
- Look up your motherboard’s model number in the driver downloads section.
- You’ll see a list of downloadable drivers.
- Go to the BIOS section and expand its menu.
- Download the latest BIOS firmware.
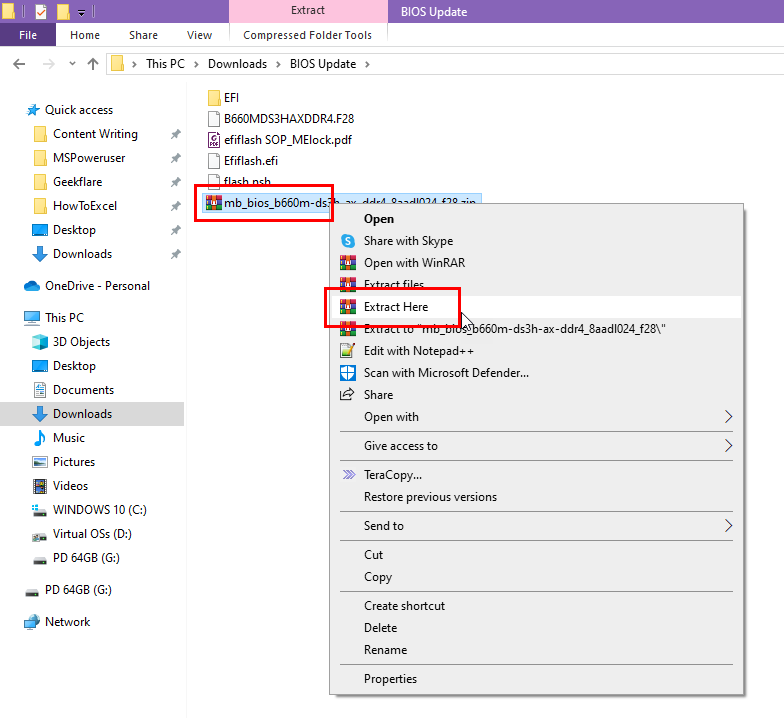
- Extract the content of the firmware ZIP file.
- Get a USB stick and format that to the FAT32 file system.
- Copy the extracted content to the USB stick.
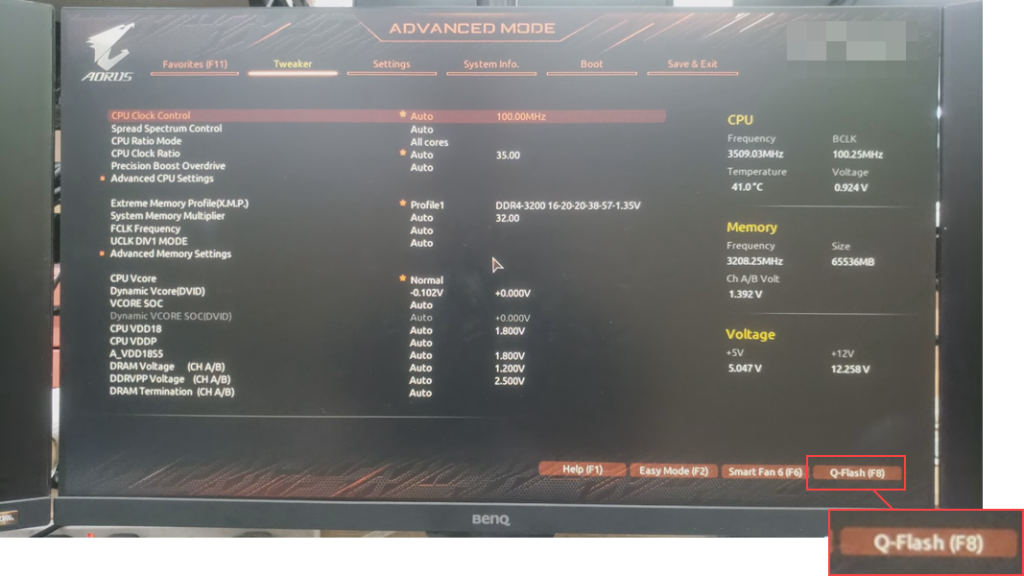
- Restart the device and go to the BIOS menu.
- Look for the BIOS update utility named EZ Flash, BIOS Management, Q-Flash, etc.
- Use the utility to select the BIOS update file on your USB drive.
- Confirm the update process.
- Once the flashing is over, your PC will reboot.
Reseat the RAM and GPU
Often, carbon disposition in the slots of GPU and RAM chips can cause irregular and slow performance of such hardware. If this is the case, the BSOD error can also show up. Do the following:
- Shut down your PC.
- Disconnect all cables including the power connection.
- Open up the left-side cover of the PC case. Usually, this is a removable cover.
- Wear an antistatic wrist strap to clear your hands of static electricity. Alternatively, touch any metal embedded in the concrete wall or earth.
- Carefully release the RAM slot lock clips.
- Remove the RAM chips.
- Unscrew the back panel of the GPU.
- Unlock the lock clip of the GPU slot.
- Remove the GPU card.
- Use a compressed gas canister to clean the slots as well as the RAM chips and GPU card.
- Snugly reseat the hardware back to their relevant slots.
- Tighten the GPU back panel screw and apply the slot locks for both the PCI Express and RAM slots.
- Close the PC case cover.
So, there you have it! You can try these methods to fix the blue screen while playing games on Windows 10 or 11 PCs for good.
Did the article help you experience BSOD-free PC gaming? Share your feedback, suggestions, and unique troubleshooting ideas in the comment box.